I have updated my Coronavirus model to include an assessment of the potential impact of the new BA.2.86 Pirola variant. The model factors in age-group structures, transmission rates, vaccination phases, and non-pharmaceutical interventions. The model finds that despite reported decreases in Covid-19 cases in the UK, case recording has been high with recent data seeming erratic, with some inadequacy in the data reported by the Office for National Statistics (ONS) after it ceased its regular reporting. I source data from Worldometers, providing reliable Covid-19 figures. The accuracy of the model may be compromised by lower reliability of active case data.
Category Archives: Worldometers
Declining Omicron cases but increasing deaths – Coronavirus
Something odd seems to be happening with the relationship between reported UK Covid-19 cases and deaths in the last few weeks, when deaths have been increasing somewhat more quickly than recently, but cases have declined steeply. My model charts seem to expose this oddity.
Tuning the age and vulnerability Coronavirus model
In my latest post on March 26th I described a new Coronavirus group model, based on work I had done as a UK case study in support of Prof. Alex de Visscher’s paper, in conjunction with Dr. Tom Sutton, on “Second-wave Dynamics of COVID-19: Impact of Behavioral Changes, Immunity Loss, New Strains, and Vaccination” which has now been published for peer review as a pre-print on Springer’s site at https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-195879/v1. I have now added the latest UK vaccination progress figures, and the UK Government’s announced intentions for the near future regarding Non Pharmaceutical Interventions (NPIs). I have also updated mortality and infection characteristics for the four different population groups in the model.
Age and vulnerability related Coronavirus modelling
In my most recent post on February 12th, I described modelling work I had done in support of Prof. Alex de Visscher’s paper, in conjunction with Dr. Tom Sutton, on “Second-wave Dynamics of COVID-19: Impact of Behavioral Changes, Immunity Loss, New Strains, and Vaccination” which has now been published for peer review as a pre-print on Springer’s site at https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-195879/v1. I have now added vaccination and multiple variants I had already added to our previous model into the new grouped population model, and this blog post reports on progress with that new model.
NPIs, Coronavirus variants and vaccine models
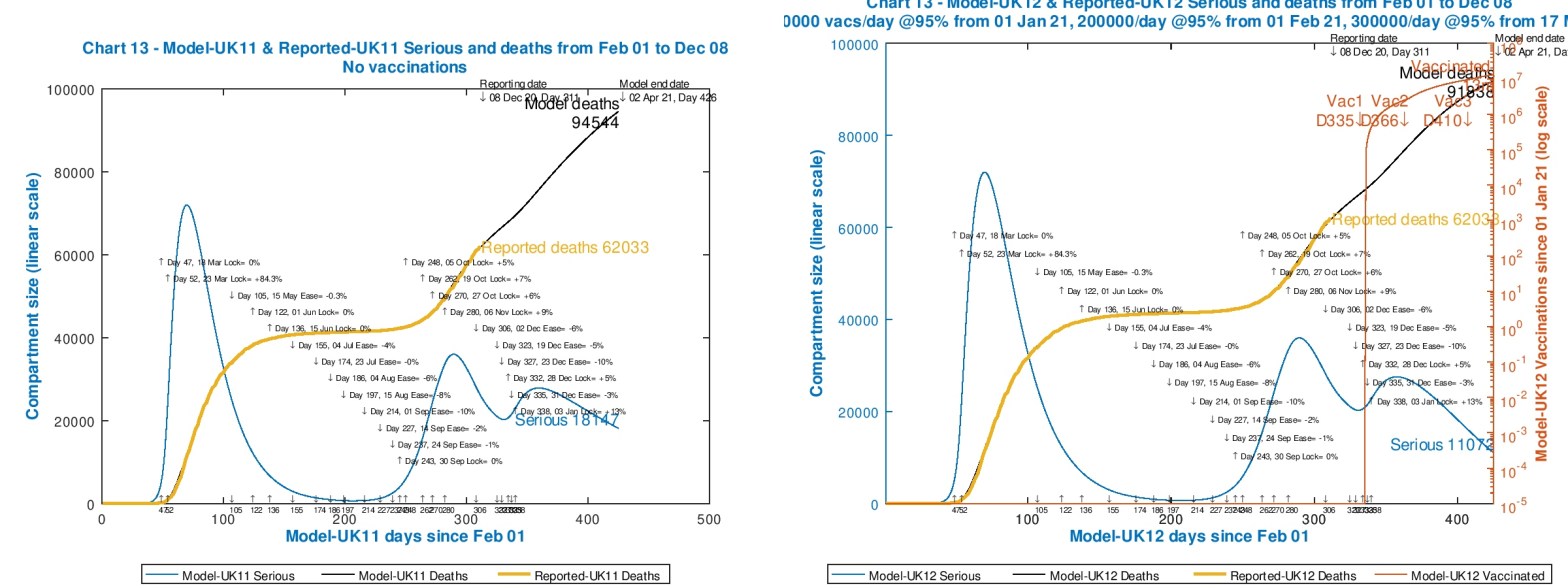
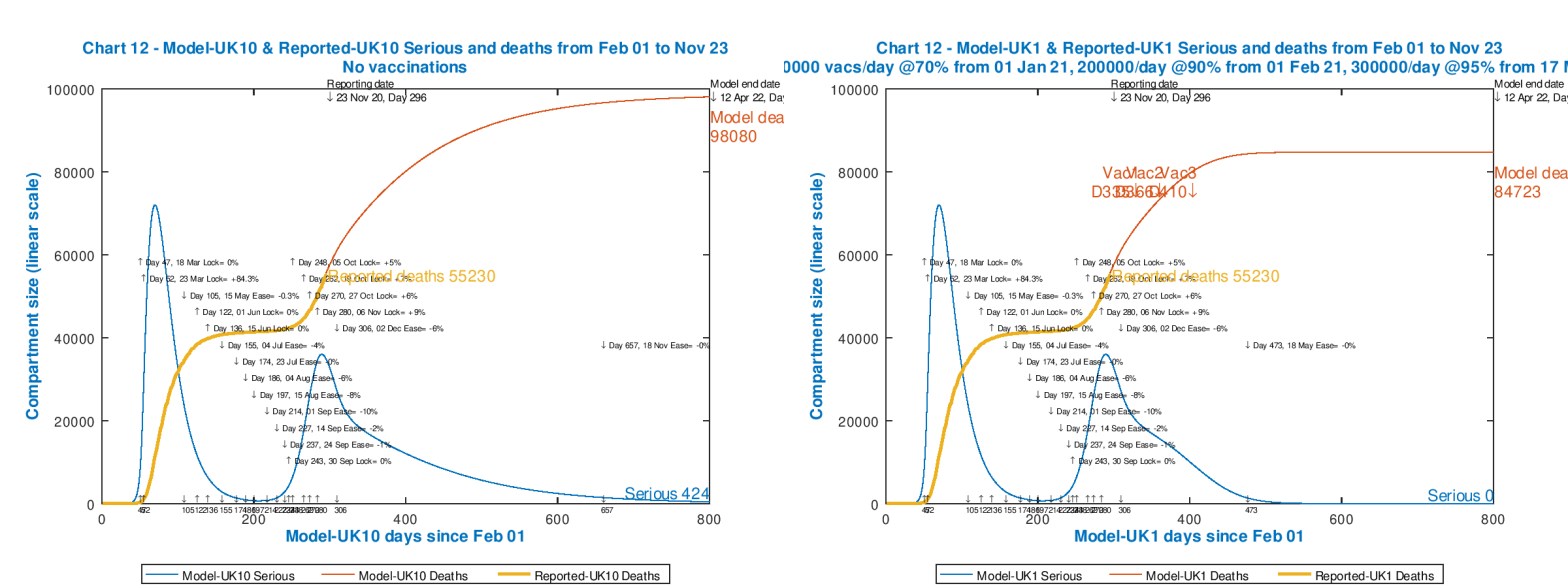
This paper reports some parametric Coronavirus model runs I have made that compare, in particular, how the UK vaccine programme allows some NPI relaxation compared with a case with no vaccination. The outcome is that the vaccine programme in the UK has the potential to reduce the imposition of NPIs on March 7th by about 15%, without costing lives, this being the next time we in the UK are due for a major NPI review, potentially involving the return of schools at around March 7th.
USA Thanksgiving Coronavirus lessons for UK Christmas and New Year?
We are aware that the rates of cases and deaths in the USA have increased steeply recently, and it seems that the natural public relaxation in precautions against Covid-19 for the Thanksgiving holiday period have exacerbated this. I have run my model with reductions to the USA intervention effectiveness during the Thanksgiving period (reflecting the increase in travel and social interactions in the USA) followed by reintroduction of the intervention effectiveness afterwards, to see the effect on the immediate projections. I have then applied similar changes to my UK models, to anticipate what the possible effect of such relaxations over the UK festive period might be. This is very much a sensitivity test of some scenarios, not a forecast.
Modelling of Coronavirus vaccine strategies
In my most recent post on November 18th, about updating my Coronavirus model to handle the impact of vaccines, I gave some examples of how case numbers, and more specifically death rates might be improved for the UK through a vaccination programme. Now that there seem to be several vaccines imminent, with efficacies ranging from 70% (Astra-Zeneca/Oxford) through 90% (A-Z/O via a different inoculation regime, and Pfizer), to 95% (Moderna) and several others in the mix, I explore some sensitivities in more detail, and also apply the model to the USA.
Make America well again – Coronavirus
I look at the impact of a postulated change in the timing of further measures to control the Covid-19 epidemic in the USA, against a current background of rapidly increasing daily case numbers and deaths. I also show an updated projection for the UK, both compared with Worldometers forecasts
Adaptive triggering and the Coronavirus epidemic life-cycle
Introduction In my last post on October 21st, looking at the potential for an exit from the epidemic, I described a cyclical version of the modelling of the epidemic in the UK, reflecting outputs from Imperial College and Harvard earlier this year, which postulated a continuing cycle of partial lockdowns, easing of restrictions and upsurgesContinue reading “Adaptive triggering and the Coronavirus epidemic life-cycle”
Where’s the exit? – Coronavirus
My title for this post is drawn from a slide I have shown before, from the 17th April Cambridge Conversation webinar, which I reported in my April 17th blog post, and also in my April 22nd blog post on model refinement, illustrating the cyclical behavior of the Covid-19 epidemic in the absence of pharmaceutical interventions, with control of cases and deaths achieved, only to some extent, by Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions (NPIs).